I Hate My Job, But Quitting Isn’t The Answer: What To Do When You’re Stuck
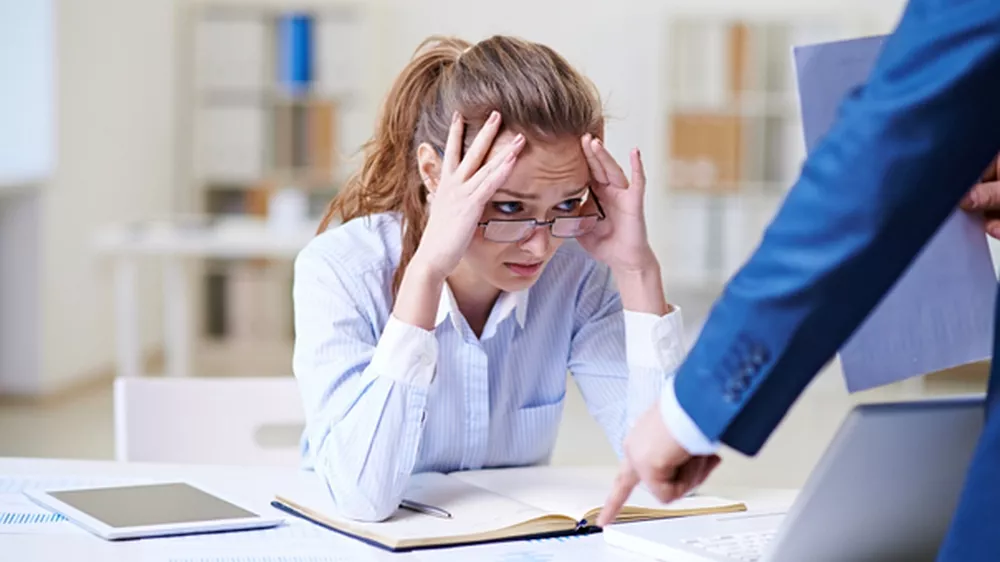
We’ve all been there. You’re stuck in a job you hate, feeling unfulfilled and uninspired. You want to quit, but you can’t because you need the money. So what do you do?
First, it’s important to understand that a career rut is not permanent. It’s normal to feel this way at some point in your career. The key is to take action and make a change. Here are some things you can do to get out of a rut:
If you’re looking for the insightful articles about financial or investment advisor, then you may want to consider Cashloanace.com to get financial decision making. Cashloanace is a blog who use their expertise to write insightful articles about tax service, developing leadership skills, personal skills and job market, wealth planning, finance, real estate investments, insurance, car loans, people struggling with debt and loans, and helping people achieve their financial goals.
Talk to your boss.
If you’re unhappy with your current situation, the first person you should talk to is your boss. They may be able to give you more responsibility or a different role within the company.
Find a mentor.
A mentor can give you the guidance and support you need to make a change in your career. They can help you identify your goals and create a plan to achieve them.
Get a new job.
If you’re really unhappy in your current role, it may be time to look for a new job. Use your network, attend industry events, and search online job boards.
Take a break.
If you’re feeling burnt out, it may be helpful to take a break from your career. This could mean taking a vacation, working part-time, or taking a sabbatical.
Make a change.
If you’re unhappy with your career, it’s up to you to make a change. This may mean changing jobs, changing industries, or starting your own business.
Making a change in your career can be scary, but it’s important to remember that you’re not alone. There are many resources and people who can help you make a successful transition.